The Advanced Reactor Roadmap, initially published in 2023, has been updated in 2025, offering expanded insights into the successful commercialization of advanced reactors. The revision includes updated status information on several key issues, identifies additional priorities, and outlines critical outcomes necessary for enabling large-scale nuclear deployment. As a living document, it will continue to evolve with new developments and stakeholder input.
Countries around the world are turning to advanced nuclear technologies to meet a wide range of national priorities, from energy security and technological leadership to decarbonization and economic development. In North America alone, there are over 60 new nuclear projects being planned today, with several having secured regulatory approvals. Construction is underway on multiple sites across the region, and some may begin operations before 2030.
The nuclear energy industry is taking action to enable nuclear energy to meet the market demand through the continued operation of existing reactors and the commercialization of advanced reactors that could be called upon to provide more than 300 GW of new generating capacity by 2050. In collaboration with other stakeholders, the nuclear industry is making significant progress toward building an orderbook for larger scale deployment. Progress can be seen through the major successes accomplished since the original report was released in 2023, including the commercial deployment of the Vogtle 3 and 4 AP 1000 units in Georgia, regulatory and legislative actions supporting accelerated deployment, significant private investment in advanced nuclear, and tech company commitments to new nuclear capacity.
The Advanced Reactor Roadmap’s intended audiences are potential customers (owners and energy offtakers), policymakers, regulators, financial institutions, public stakeholders, Indigenous rights holders, and industry stakeholders. The roadmap—developed through a multistakeholder process, including experts from advanced reactor developers, suppliers, utilities, researchers, and industry associations—describes an achievable path to facilitate the successful commercialization of advanced reactors, spur and support the necessary actions, and enable deployment at the levels needed.
The approach that the industry is taking to enable the value of advanced reactors to fulfill critical market needs is focused on three key things:

Commercializing advanced reactor technologies that deliver the desired value

Establishing a portfolio of advanced reactor technologies to meet a diverse set of market and customer needs

Ensuring that the commercialization of these technologies is both cost-effective and on track to meet the milestones for decarbonization on time
The approach relies on disruptive innovations that develop advanced reactors with benefits that deliver value to the market, including easing deployment challenges, accelerating deployments, and increasing cost-competitiveness, all while increasing safety and maintaining reliability. This requires the industry to change how it designs, deploys, and operates advanced reactors. The approach is framed to allow a realistic, phased, and risk-managed approach to deploying advanced nuclear technology. This approach of establishing, advancing, and expanding (EAE) to scale (see Figure 1) is the basis for pursuing industry priorities by setting up early wins, derisking for owners, and creating fast followers.
“The approach is framed to allow a realistic, phased, and risk-managed approach to deploying advanced nuclear technology.“
Continued industry leadership is essential to execute and drive the strategy, promote collaboration and coordination, and ensure that actions are being completed on the roadmap, which need to be taken now to ensure that the future energy demand can be met. Industry leadership must articulate a vision that builds confidence, attracts capital and investment, inspires the industry to overcome the inevitable challenges, brings technology to the market, and achieves the needed large-scale deployments. The deployment of over 300 GW of new nuclear capacity is only possible through persistent effort.
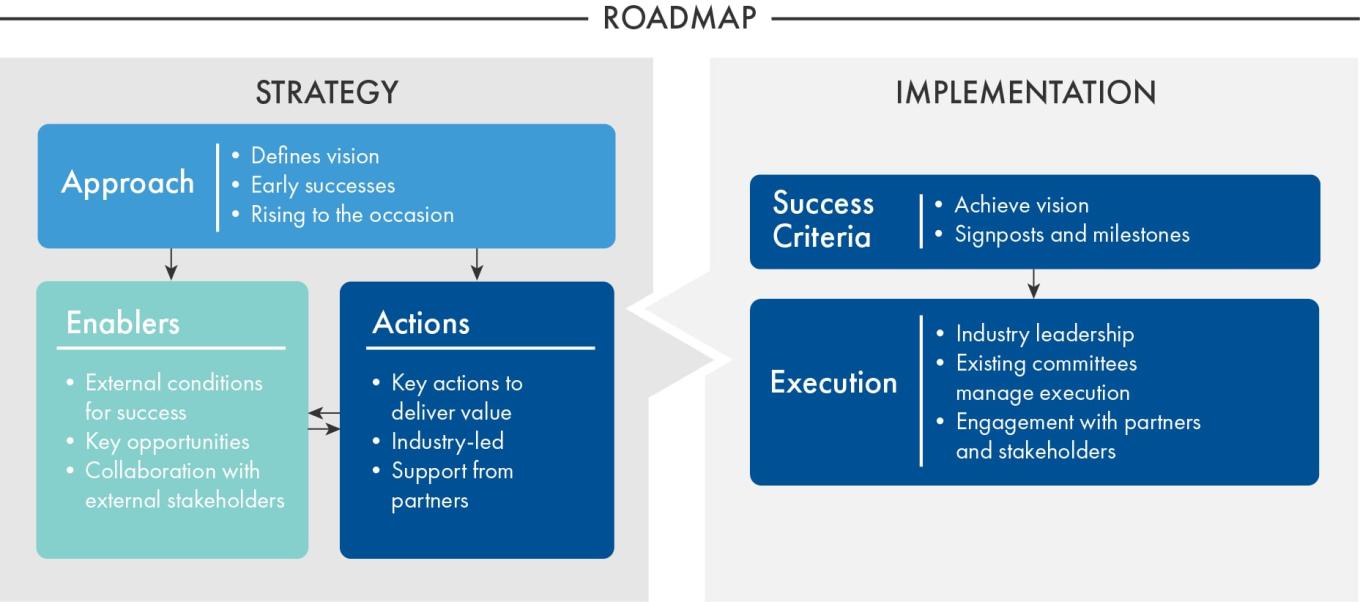
The roadmap presents a foundational approach to meeting market demand, built around two main components: 1) conditions that would further enable advanced reactors to meet market needs (called enablers), and 2) the key issues that the industry plans to address to deliver advanced reactors into the market.
ENABLERS
Enablers are the conditions related to policy, regulatory, and public acceptance surrounding the commercialization of advanced reactors and are key opportunities for stakeholders and the industry to enable and enhance the deployment of advanced reactors.
There are seven enablers

First Mover Success

Fast Followers

Regulatory Efficiency

Siting Availability and Permitting

Indigenous and Public Engagement

Supply Chain Ramp-Up

Workforce Development
KEY ISSUES
Key issues are those issues the industry needs to address to deliver value in the deployment of advanced reactors. The industry actions focus on what the industry can control in delivering a timely portfolio of products with value that the market desires.
There are a total of 49 key issues organized into 13 strategic elements, which are grouped into the following three issue pillars.

Regulatory Efficiency

Technology Readiness

Project Execution
These key issues are further prioritized to identify the high-priority issues that make the greatest contribution to delivering value to the market and other key issues that could help further improve success. This roadmap is intended to be a valuable, informative asset in enabling that outcome.